
ShareMyRadiology 放射线学 Sigmoid volvulus
The large central lower-abdominal gas-filled viscus represents the distended sigmoid colon that has volved at its mesenteric base causing obstruction. On the coronal reformat of the CT, the swirling pattern of the vessels at the base of the mesentery is seen and confirms the cause of sigmoid distension. Features here are of sigmoid volvulus.

Abdominal Xray showing Sigmoid Volvulus with Steel pan pattern. Download Scientific Diagram
sigmoid volvulus causes obstruction of the distal large bowel; therefore, the ascending, transverse and descending colon may be dilated few air-fluid levels may be seen 1 Cecal volvulus arises in the right lower quadrant extends towards the epigastrium or left upper quadrant colonic haustral pattern is maintained

Pearls and Pitfalls in Multimodality Imaging of Colonic Volvulus RadioGraphics
Radiographic features Cases in Radiology: Episode 6 (abdominal emergency, x-ray, CT) Watch on Two types of caecal volvulus are described although, in practice, the distinction is not clinically relevant: axial torsion (described below) caecal bascule Plain radiograph
Cecal volvulus Image
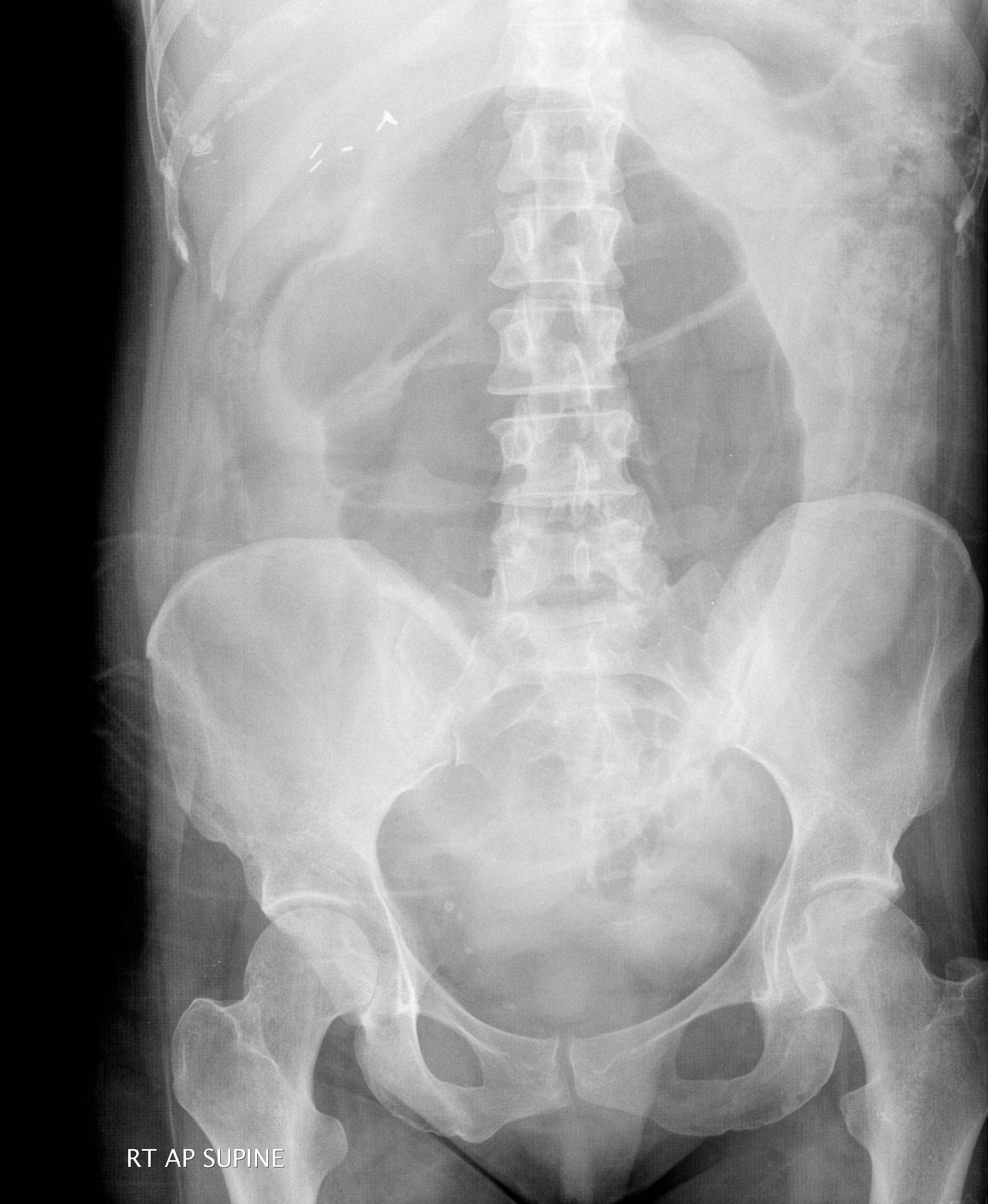
Caecal volvulus Hover on/off image to show/hide findings Caecal volvulus The caecum is grossly dilated and is no longer located in its anatomical position, the right iliac fossa ( RIF ), which is occupied by small bowel in this example. Caecal volvulus - 'Caecal embryo' sign Hover on/off image to show/hide findings Caecal volvulus
Caecal volvulus Radiology at St. Vincent's University Hospital
Pathophysiology — Sigmoid volvulus occurs when an air-filled loop of the sigmoid colon twists about its mesentery. Obstruction of the intestinal lumen and impairment of vascular perfusion occur when the degree of torsion exceeds 180 and 360 degrees, respectively [ 24 ]. A variant of sigmoid volvulus (ileosigmoid knotting) occurs when the.

Sigmoid volvulus Image
This condition most commonly presents in patients who are less mobile; who are bedbound and institutionalized; and who usually have a history of chronic constipation. [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] Sigmoid.

Volvulus of the Gastrointestinal Tract Appearances at Multimodality Imaging RadioGraphics
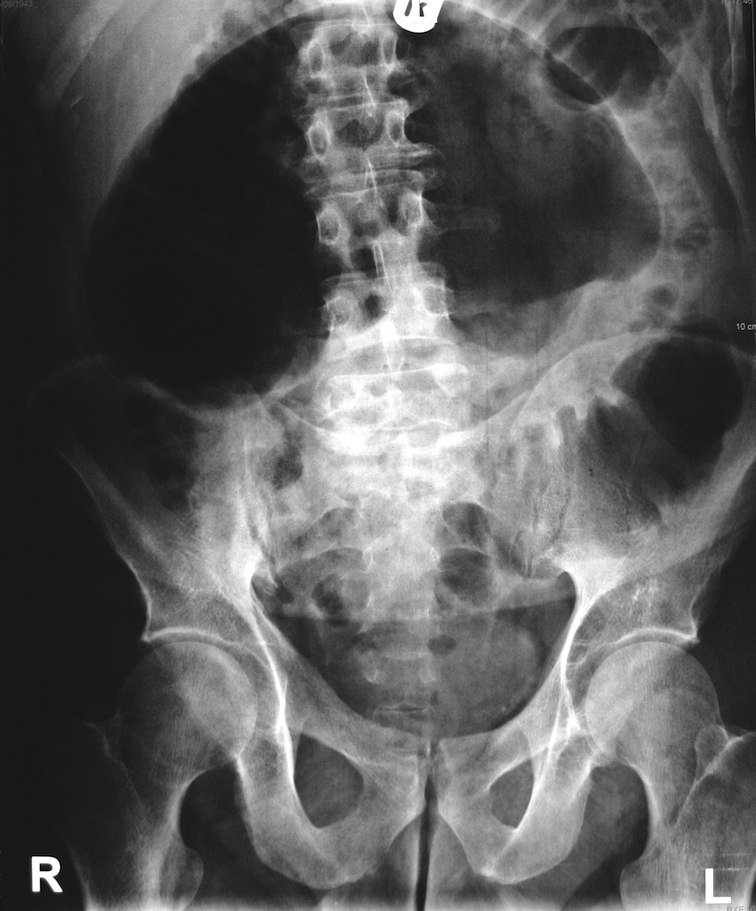
Radiographic features Cases in Radiology: Episode 6 (abdominal emergency, x-ray, CT) Watch on Two types of cecal volvulus are described although, in practice, the distinction is not clinically relevant: axial torsion (described below) cecal bascule Plain radiograph
Colonic Volvulus Radiology Notes
Volvulus of the transverse colon, splenic or hepatic flexure, or other types are rare (less than 1% of cases). If left untreated, colonic volvulus can result in significant morbidity and mortality. Colonic volvulus is a challenging clinical diagnosis, and it is typically made after performing imaging.
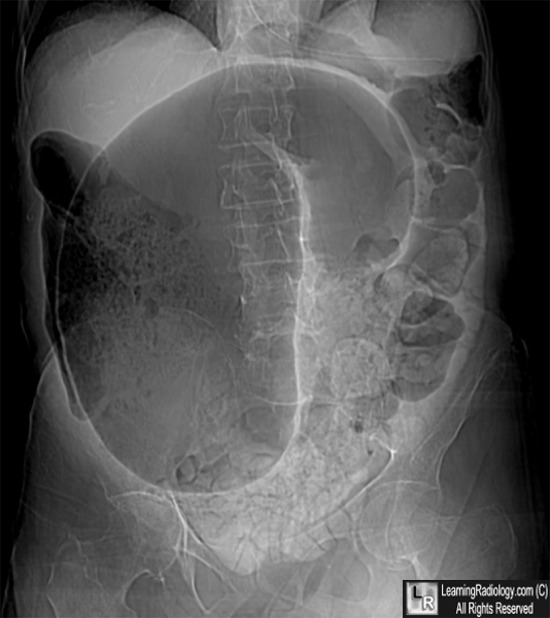
Cecal Volvulus Radiology Key
Gastric volvulus is a specific type of volvulus that occurs when the stomach twists on its mesentery. It should be at least 180° and cause bowel obstruction to be called gastric volvulus. Merely gastric rotation on its root is not considered gastric volvulus. Epidemiology

XRay Abdomen (erect) depicting the Coffee Bean sign of sigmoid volvulus. Download Scientific
Treatment Volvulus occurs when part of the intestine loops around and folds over itself. It often happens in the cecal and sigmoid colon sections of the intestines. The twisting can cut off the tissue's blood supply, leading to symptoms such as extreme pain, bloody stool, and bowel obstruction.
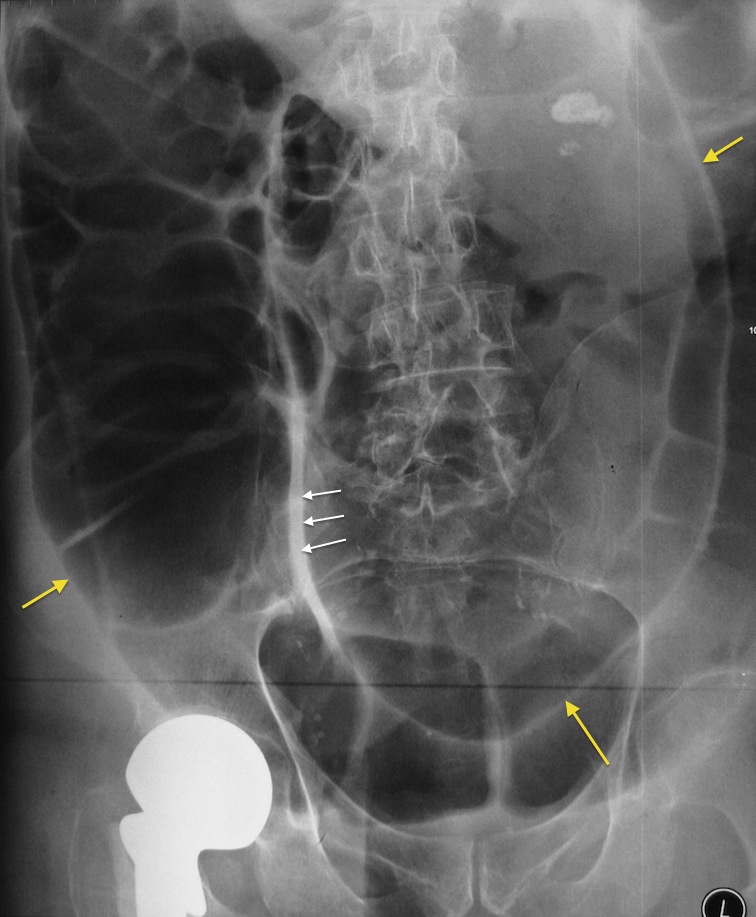
Sigmoid volvulus Radiology at St. Vincent's University Hospital
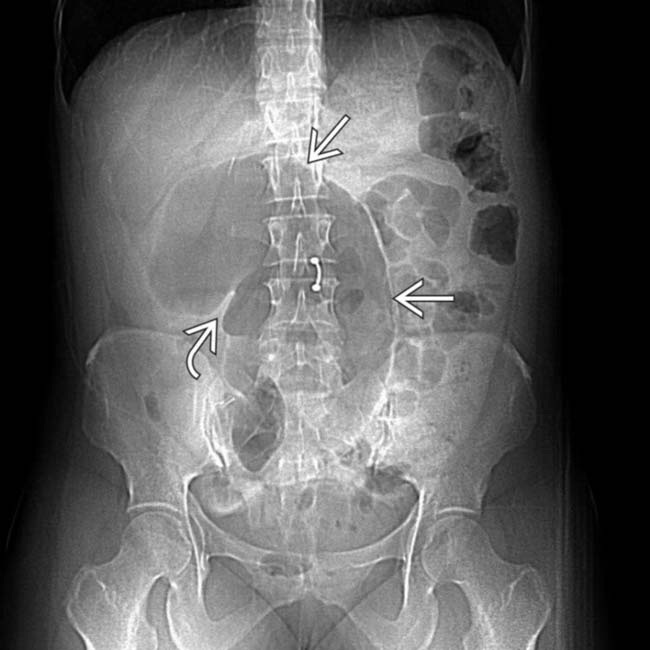
Sigmoid volvulus with coffee bean sign as seen on abdominal X-ray. Sigmoid volvulus is due to a twist at the base of the sigmoid mesentery which is a fixed position in the left iliac fossa.

Caecal volvulus after cardiac surgery BMJ Case Reports
Intestinal malrotation is an entire spectrum of rotational and fixation disturbances that can occur during embryonic development. The anatomic variant that poses the highest risk of volvulus is a narrow midgut mesenteric base accompanied by lack of retroperitoneal midgut fixation. This variant cannot be reliably determined from any radiologic.
Cecal volvulus causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
Sigmoid volvulus: coffee bean sign ( bent inner tube sign /inverted U sign, kidney bean sign ): dilated loop of bowel ( sigmoid colon) with absent haustrae that arises in the left lower abdomen and extends towards the right upper abdomen. Proximal colonic small bowel air-fluid levels. rectum. Cecal volvulus: dilated loop of bowel ( cecum) with.

Volvulus Malrotation
A volvulus is a twist of the intestine around the axis of its blood supply. In the case of a sigmoid volvulus, the twist occurs in the sigmoid mesentery at its base. Sigmoid volvulus is the most common type of volvulus of the colon. Less common are caecal volvulus and volvulus of the transverse colon.
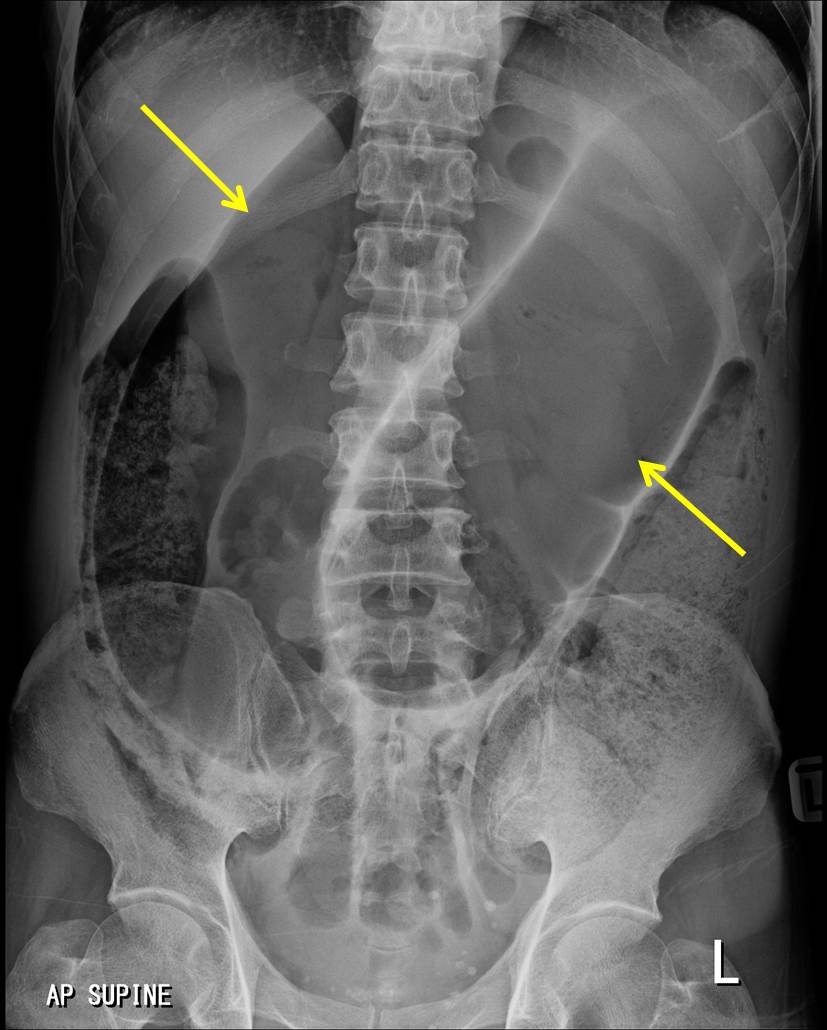
Sigmoid volvulus Radiology Cases
Intestinal volvulus is a broad term that describes the torsion of bowel around its mesentery. Torsion results in narrowing of the lumen at the point of rotation and compromise of the vessels that supply the torsed gut.

Volvulus of the stomach, barium Xray Stock Image M290/0159 Science Photo Library
Intestinal malrotation: arrest in the normal rotation of the gut in utero, resulting in an abnormal orientation of the bowel and mesentery within the abdominal cavity. Common types of intestinal malrotation [3][4][5] Nonrotation. Incomplete rotation. The entire colon is left-sided; the entire small bowel is right-sided.